Metal transfer in which molten metal from a consumable electrode is propelled axially across the arc in small droplets. See Figure S-23. See also GLOBULAR TRANSFER and SHORT CIRCUITING TRANSFER.

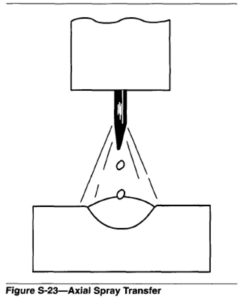
When using argon, or an argon and oxygen mixture, as a shielding gas with the gas metal arc welding (GMAW) process, spray transfer is the result of a pinch effect on the molten tip of the consumable welding wire. The pinch effect physically limits the size of the molten ball that can be formed on the end of the welding wire, and therefore only droplets of metals are transferred rapidly through the welding arc from the wire to the workpiece. The droplets produced in the spray transfer method are equal to or smaller than the diameter of the wire being used. See PINCH EFFECT, GLOBULAR TRANSFER. and GAS METAL ARC WELDING.
