At a constant volume, the pressure of a perfect gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature; or at a constant pressure the volume is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. This is expressed as follows:
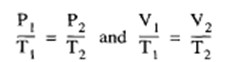
in which T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures, respectively. (The absolute temperature in degrees Fahrenheit is [460 + TI where T is the observed temperature in degrees F).
